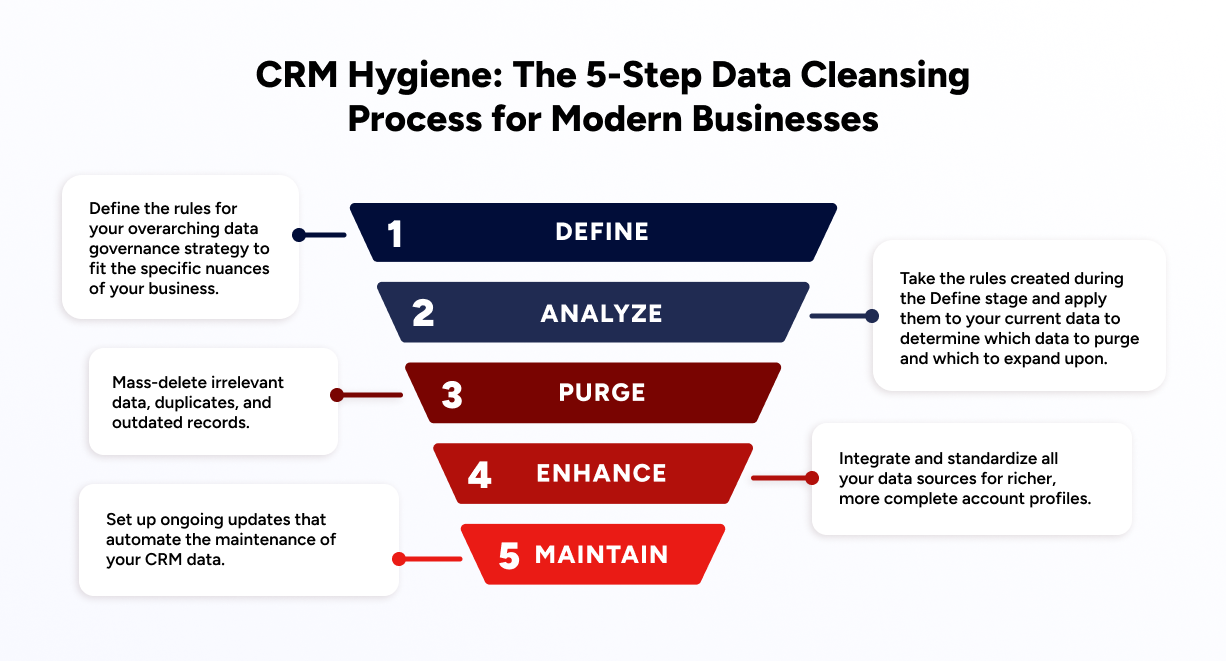
Before solving their biggest CRM cleansing challenges, go-to-market teams need to define the rules of engagement for their data. The idea is to keep a living, breathing CRM that’s constantly being updated with customized rule-based workflows — a CRM that’s always “on.”
To make this a reality, all businesses need to tailor their data hygiene strategy to fit their unique processes, goals, and requirements. Properly defining these factors is a critical first step that helps make sure you’re only spending resources on the most relevant customer segments with the highest profit potential.
The Define stage — the first official step in a comprehensive five-part CRM cleanup process — requires answering a few key questions, followed by the application of sophisticated software powered by rule-based workflows that help you apply these rules at scale.
The CRM Hygiene Series
This blog is part of a comprehensive series of guides that dive deeper into each of the five steps in the CRM data hygiene process. Navigate to each step to learn more about each step, including how to apply them, why they’re necessary, and the technical aspects of it all below.
Get the Downloadable Version of Our 5-Step CRM Hygiene Guide:
How To Make Sure You’re Getting the Most out of Your Best Data
Before defining rules, here’s a deeper dive into the data points that need to be identified.
1. What is the Total Addressable Market of Businesses for Your Products or Services?
What this step does: Finding your TAM calculates the overall number of business professionals or entities that could potentially use your product or service.
Why it matters: Understanding the size of your market allows for more accurate forecasting and goal setting so that your business strategies are realistic and grounded in potential market reach.
What results to expect: This step enables a clear picture of the market opportunity available to your business that’ll guide what data you’ll clean.
How to do it: Conduct market research and data analysis to estimate the number of business professionals and entities that fit the criteria for your offerings. Consider firmographic factors like industry, revenue, size, and geographic location.
A technical example
Say you’re a Salesforce app startup and you know that you can only sell to Salesforce customers. At this stage, you likely aren’t going to sell to enterprise businesses. However, your app specifically caters to software companies, which means you need a third-party data provider that provides technographic as well as firmographic data attributes to help you identify your Total Addressable Market (TAM). |
2. What is the Ideal Customer Profile Within Your Total Addressable Market?
What this step does: This step identifies the specific characteristics, needs, and behaviors of the businesses who are most likely to find value in your products or services, representing your ideal target market within your broader Total Addressable Market.
Why it matters: Once you know you’re targeting prospects with the highest potential for conversions and long-term loyalty, it becomes easier to tailor sales and marketing efforts with more precision.
What results to expect: Finding your ICP aligns your product offering with real customer needs. It sets your business up for improved marketing and sales campaigns, higher conversion rates, and increased customer satisfaction.
How to do it: Analyze your existing customer base to identify commonalities among your most valuable customers, including demographic information, industry sectors, company size, decision-maker roles, and purchasing behaviors. Then, use this data to create a detailed ICP that guides your targeting strategies.
A technical example
You start by enriching your data with robust tools like ZoomInfo. Next, analyze your best and worst customers to find common traits, and use this data to build a model for your ICP. You then create lists of potential target accounts and key personas. To make sure you aren’t purchasing duplicate data, use ZoomInfo’s List Import feature. Tag target accounts and categorize lead job titles using Mass Update. Then, Match leads to accounts and convert key personas into contacts using ZoomInfo’s Lead to Account functionality. Be sure to enrich these contacts with relevant data points — like phone numbers, emails, job titles, or social profiles — to get a more complete view of your ICP. Develop a multi-channel outbound strategy to drive inbound interest, and use analytics to identify the most effective marketing channels for attracting leads that fit your target account profile. Continue to adjust your campaign strategies based on these insights. |
3. What is the Total Addressable Market of Business Professionals for Your Products or Services?
It’s time to identify the contacts within the businesses in your TAM that you’ll be selling to.
What this step does: Estimates the maximum number of business professionals that could potentially decide to purchase your products or services.
Why it matters: Knowing your TAM for business professionals helps set realistic sales targets and allocate marketing resources more effectively. It makes sure your offering is aligned with market potential.
What results to expect: A foundational understanding of the market’s size helps in strategic planning, budgeting, and forecasting. You’ll have a data-driven foundation to make more informed decisions about messaging, marketing strategies, and sales goals.
How to do it: Use demographic data to assess the number of business professionals or in your targeted sectors. Analyze factors like market trends, competitor analysis, and economic indicators that influence the purchasing behavior of these professionals.
A technical example
To determine the TAM of business professionals for your product or service, start by building out the buying committee so you don’t have to work with isolated contacts. Remember, these are professionals within the companies inside your TAM. You need to enrich the contacts you have (say, at director and above) and create any contacts you don’t have with ZoomInfo tools like Discover, which help you fill in missing contact data fields. |
4. What is the Ideal Persona Profile Within Your Total Addressable Market?
What this step does: This step crafts a detailed description of the archetypical business professional or decision-maker within your TAM who is most likely to buy your product or service based on their needs, challenges, and influence within the business.
Why it matters: Creating an Ideal Persona Profile enables you to personalize your marketing and sales approaches to individual contacts more precisely, leading to better engagement, higher conversion rates, and stronger customer relationships.
What results to expect: This step enables tailored marketing messages and sales strategies that resonate deeply with your target persona, leading to more effective lead generation, improved customer acquisition costs, and higher ROI on marketing efforts.
How to do it: Collect and analyze data from your current customer base, market research, first-party data, and sales interactions to identify common characteristics, pain points, and purchasing triggers of your most successful engagements.
Use this information to build a persona profile that guides content creation, communication strategies, and messaging tailored to meet the specific needs of this group.
A technical example
To pinpoint your business persona archetype within your TAM data, segment your contact data by relevant attributes like job title, department, persona, and seniority level. Enrich the data for these key personas using tools like ZoomInfo Data Enrichment, gathering information such as device IDs, contact details, and social media profiles. Then, take it a step further and use tools like ZoomInfo Discovery to create contacts in your TAM not currently in your CRM. |
5. Create Duplicate Definitions
What this step does: Here’s where you integrate data standardization, or normalization, into your CRM cleansing efforts to improve data quality across the board. It makes sure that all data entered into the CRM follows a consistent format, reducing the amount of bad data due to human error or varied data entry methods.
Why it matters: Bad data leads to ineffective communication efforts, customer dissatisfaction, and ultimately, customer loss. It’s why standardizing your data is crucial for maintaining high-quality data, which fuels high-quality GTM motions, yet is often overlooked during CRM implementation discussions.
What results to expect: You’ll work with a significant reduction in bad data, including fewer duplicates, more accurate reporting, and better customer engagement efforts. Data standardization leads to a cleaner, more reliable database that supports effective decision-making and virtually error-free operations.
A technical example
You have data, but it needs to be standardized. To get started, create a deduplication task in a data management solution like ZoomInfo, starting with the identification and merging of duplicate leads. Use custom matching rules to ensure accurate identification of duplicates based on specific fields like email and company name. By applying master record rules, you prioritize data from specified systems based on its higher data integrity, making sure the surviving records retain the most accurate and comprehensive information. You use the protected data feature to safeguard sensitive account information linked to your ERP system, preventing any unintentional data loss during the merge process. Finally, schedule the deduplication task to run during off-hours, minimizing operational disruptions. |
6. Create Duplicate Survivorship Rules
What this step does: Creating survivorship rules sets guidelines to determine which data records to retain when duplicates are identified, ensuring the most accurate and comprehensive information is preserved.
Why it matters: Survivorship rules prevent the loss of valuable information during the deduplication process, maintaining data quality and integrity in your CRM.
Imagine your CRM system holds two records for the same customer: “John Doe” from “john.doe@example.com” and “J. Doe” from “johnd@example.com.” Each record contains unique interactions and transaction histories that are crucial for your sales strategy and customer service.
Without explicit duplicate survivorship rules, a deduplication process might mistakenly discard one record entirely, losing valuable insights about John’s preferences and interaction history.
What results to expect: A cleaner, more reliable database where each record represents the most complete, up-to-date information available, enhancing decision-making and customer engagement.
A technical example
Let’s say you need to create a survivorship rule that only keeps valid contact emails. Within your data platform, create a new duplicate survivorship rule by selecting the entity and naming it. Define the criteria for the surviving data, like company name, and save the rule. ZoomInfo allows data professionals to create specific criteria for survivorship rules. These are: Surviving Field Value Rules: These rules determine which field value will survive the merge for specific fields. They function as exceptions to the master record rules for the fields that are configured. For example, you can retain the oldest record as your master but take the phone and email values from the newest record to have the most current contact information. Archive Field Values: By archiving field values that have been overwritten, you can retain important data that would have been lost during the merge in a text field such as comments or description. Create as many rules as necessary to make sure each field is filled in with the relevant data you want to keep. For example, you could create a survivorship rule that adds behavioral scores together. Or you could set a rule to always take the greater value for company revenue. |
7. Create Matching Rules
What this step does: Matching rules define criteria for identifying duplicates within your database, such as matching email addresses, phone numbers, or names.
Why it matters: Accurate matching rules are crucial for effectively identifying duplicates, ensuring that your CRM cleansing efforts target the right records.
What results to expect: You’ll work with fewer instances of duplicate data, leading to improved data quality and a more efficient, effective CRM system.
A technical example
To set up matching rules effectively, begin by accessing your data management platform and navigating to the default matching rule templates. These templates, or your custom logic, play a crucial role in pinpointing and grouping duplicate records. By using conditional logic and configuring field matchers, tailor the system to recognize duplicates based on specific criteria. Then, enhance the matching process by combining several matchers, using the power of related records to consolidate leads from identical companies under a single lead owner. For more nuanced differentiation, employ subdomain matching to link website URLs sharing the same domain but differing in subdomains.Before finalizing, thoroughly review your Deduplication Task, then export and merge identified duplicates. |
8. Create Enrichment Survivorship Rules
What this step does: Enrichment survivorship rules set guidelines for integrating external data sources during the enrichment process, ensuring consistency and accuracy in the updated records.
Why it matters: These rules help maintain the integrity of your CRM data by determining which external data is reliable and should be merged with existing records.
What results to expect: The resulting database is both richer in detail and more accurate, providing a solid foundation for productive marketing, sales, and customer service efforts.
A technical example
With a sophisticated data management platform, you’re able to easily create enrichment survivorship rules by selecting one of the following three rules per field: Do not update: Choosing “do not update” is best for instances where you don’t want to change data like the address on a customer account. Since the address is already in a billing system, for example, this means changing the address in a current subscription could lead to errors like missed tax charges. Update if blank: Choose this enrichment survivorship option if there is no value in the field you’re mapping so it can be updated. Overwrite: If you want to keep overwritten field values, choose Overwrite to archive them in a secondary field. This is a critical step in case of errors. For example, overwritten email addresses should be archived in case you’re incorrectly overriding a good email with a bad one. |
9. Create a Naming Convention for Businesses, Departments, Titles, Industries, and More
What this step does: Naming conventions standardize formats for naming and categorizing key data points such as business names, department names, job titles, and industry types within your CRM.
Why it matters: Consistent naming conventions eliminate ambiguity and inconsistency, making data easier to manage, analyze, and use across your business.
What results to expect: Setting naming conventions leads to streamlined data retrieval and analysis processes. The result: Better operations based on clearer data for insights into business performance and market trends.
A technical example
You’re ready to set up your naming convention after your team has established a clear and consistent naming convention for your records, tasks, and objects. These naming conventions should include specific details that are relevant to your business needs. Apply the naming convention across your business records, tasks, or objects. Now, you’re sure that all your data is named consistently, according to the conventions you established earlier. It’s important to periodically review and update your naming conventions as needed. |
10. Create Record Assignment Rules
What this step does: These are the predefined rules that will ensure records are assigned accordingly — like clockwork. Setting this rule will make sure new and existing records are assigned to the appropriate team members or departments.
Why it matters: Effective record assignment ensures that leads, customers, and tasks are quickly directed to the right people, improving response times and customer satisfaction.
What results to expect: Expect a boost in team productivity and better customer relationship management, as records continue to get systematically organized and directed to the appropriate parties for action.
A technical example
To create record assignment rules, set up automated, rules-based routing to assign leads. These rules are customizable, combinable, and easy to create. Define the criteria and rules for routing based on your segmentation within the database. Then, add new rules and establish their criteria based on the Territory field on new Leads (e.g., Northeast or Northwest). Set the new lead owner to a specific user based on the established criteria. Make sure all configurations are set correctly to enable seamless processing and assignment of records across your systems based on time zones or working hours. |
Next Step in the CRM Hygiene Process: Analyze Your Data
The Define phase of establishing a clean CRM sets the stage to creating a CRM that makes sure your data doesn’t go stale and reflects the changes, growth, and dynamism of the real-world market you’re setting out to address.
At this stage, you’re defining the rules of engagement — definitions are the “rule of law” that keep the order within your database as it grows, evolves, and ingests data from several sources.
Once finished, the next step, Analyze, helps us understand what data can eventually be purged from your database.