Turning raw data into actionable insights unlocks high performance for sales and marketing teams. But only if your data is reliable.
Maintaining strong data quality requires continuous cleaning, correcting, and prevention. The most effective approach: enriching your database with verified information and stopping errors from entering in the first place.
Here's how to ensure your go-to-market teams have the high-quality data that sets them apart.
What Is Data Quality?
Data quality measures how accurate, complete, consistent, and current your business information is. It determines whether your data can be trusted for decision-making, reporting, and operational execution.
For go-to-market teams, this translates to contact records, account data, and CRM fields that revenue teams depend on daily. When data quality is high, your team can act on it with confidence.
Data Quality Management
Maintaining high data quality is an ongoing task. Information that is correct today can easily become outdated tomorrow, and that's assuming every record was perfect to start with.
Data quality management creates systems to maintain reliability through:
Guidelines: Standards for data collection and storage
Validation: Rules to ensure accuracy and reliability
Maintenance: Data profiling, auditing, cleansing, and monitoring
While these processes help any business, they become critical as data volume grows. Without a system in place, data quality decreases rapidly.
Good data management ensures everyone has information they can rely on. This trust is the foundation for fact-based decision making.
Why Is Data Quality Important for Go-to-Market Teams?
Bad data costs businesses real money. Poor quality data costs larger businesses millions of dollars per year in missed opportunities and technical hurdles.
The time cost is equally brutal. Data scientists spend a significant portion of their time manually cleaning datasets instead of generating insights.
For GTM teams specifically, poor data quality creates operational friction that directly impacts revenue:
Bounced emails: Invalid contact data wastes outreach and damages sender reputation
Misrouted leads: Incorrect territory or account assignments slow response time
Duplicate records: Inflated pipeline counts distort forecasting
Stale firmographics: Outdated company data breaks segmentation and targeting
When data quality suffers, so does decision-making quality, operational efficiency, customer trust, and ultimately, revenue impact.
The Six Dimensions of Data Quality
Data quality has multiple dimensions. Business leaders who wish to improve data governance need to consider the following:
Accuracy
Accuracy means data correctly reflects real-world entities. For GTM teams, this translates to correct job titles, valid email addresses, and accurate phone numbers. When a contact record shows someone as "VP of Sales" but they're actually a Director, outreach messaging misses the mark.
Completeness
Completeness means all required fields are populated. Contact records with missing phone numbers or company records lacking revenue data cannot be properly scored, routed, or prioritized. Incomplete data forces manual research or causes opportunities to slip through the cracks.
Consistency
Consistency means uniform data formats and values across systems. When "United States" appears as "US" in one system and "USA" in another, segmentation breaks. Marketing automation, CRM, and downstream tools need consistent values to function properly.
Timeliness
Timeliness means data is current enough for its intended use. A contact who changed jobs six months ago represents wasted outreach and a missed opportunity at their new company. B2B data decays quickly, making continuous refresh critical.
Uniqueness
Uniqueness means no duplicate records exist in the dataset. When the same account appears three times in your CRM, pipeline reports inflate and account ownership becomes unclear. Deduplication is essential for accurate reporting.
Validity
Validity means data conforms to defined business rules and formats. Email fields should require proper email format, not accept any text string. Industry codes should match a defined picklist. Validation rules prevent bad data from entering your systems in the first place.
An assessment that includes all these dimensions provides a good snapshot of your data quality. However, the picture can change quickly.
This is partly because data is rarely left untouched. Salespeople are constantly accessing customer data. Automation tools draw on database records to complete tasks. Executives need the latest information to make decisions.
Over time, those processes can interfere with data consistency and accuracy. To prevent these problems, it's essential to have management and maintenance processes throughout the data lifecycle.
Data Quality vs. Data Integrity
While related, data quality and data integrity address different aspects of data reliability:
Data quality: Attributes of the data itself. Is it accurate, complete, timely?
Data integrity: Trustworthiness of data throughout its lifecycle. Is it protected, consistent across systems, traceable?
Data quality refers to attributes of individual records: accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Data integrity refers to the reliability and trustworthiness of data throughout its lifecycle, including protection from corruption, unauthorized changes, and system failures.
Both matter for GTM teams. Quality ensures your data is useful. Integrity ensures it stays that way.
Common Data Quality Challenges
Even data-aware companies struggle to maintain quality at scale. GTM teams face three core obstacles:
Data Silos and Fragmented Systems: When sales, marketing, and customer success operate in isolation, data becomes inconsistent across CRM, marketing automation, and downstream tools. The same record can exist in multiple states. Without system integration, there's no single source of truth.
Data Decay and Timeliness: B2B data decays quickly due to job changes, company restructures, M&A activity, and business closures. Data that was accurate at collection becomes stale without continuous refresh. Manual updates can't keep pace with the rate of change.
Volume and Velocity: The sheer volume of data and speed of change outpaces manual quality checks. As companies scale their GTM motions, data quality processes that worked at smaller scale break down. Automation becomes necessary, not optional.
How to Measure Data Quality
Data quality metrics and KPIs show you whether your data is reliable or degraded.
Key Data Quality Metrics
Track these metrics to assess your data reliability:
Match rate: The percentage of records in a dataset that can accurately be linked or matched to a corresponding record. A good score means consistent data and good mapping.
Fill rate: The ratio of populated (or non-null) data values in a dataset compared with the total possible values for a given field. A high rate means there is minimal missing information.
Match confidence: The level of certainty that a matched record is the right one, usually expressed as a score or percentage. A high score indicates high confidence.
Completeness rate: Percentage of required fields that contain valid data across your dataset.
Duplicate rate: Percentage of records that are duplicates in your system.
By multiplying data quality characteristics, you can calculate a dataset's reliability rating, or how trustworthy it is.

Data Profiling and Validation
Data profiling involves reviewing datasets to identify anomalies, missing values, and format violations. Validation applies rules to enforce standards before data enters your systems. Together, these practices enable ongoing monitoring and continuous improvement.
How to Improve Data Quality for GTM Teams
Even in the most data-aware companies, reliability is rarely perfect. What's more, the majority of businesses miss this mark.
Maintaining good data quality is even harder when drawing information from multiple sources. Thankfully, there's a clear path to improving GTM data quality through smart orchestration:
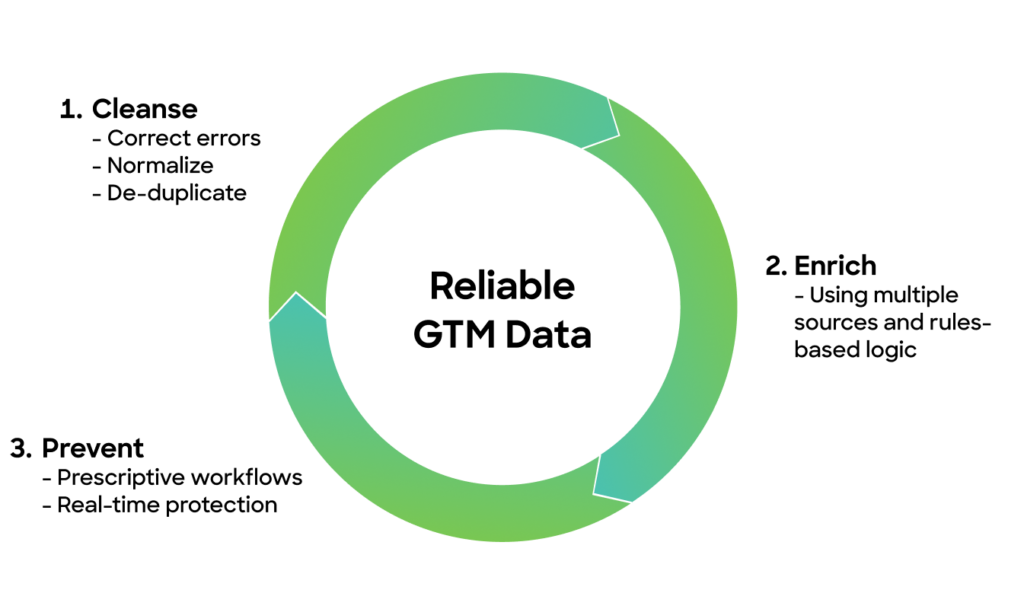
Cleanse and Standardize Your Data
A data normalization (or data standardization) process is necessary for data that enters a system through various touchpoints.
This process groups similar values into one common value for streamlined processing, distributing, and analysis. Data normalization is necessary because it provides semantic consistency across your GTM systems.
In addition, the data cleansing step (a.k.a. remediation) can involve correcting inaccuracies, such as spelling mistakes in data records, and removing duplicate data to free up resources.
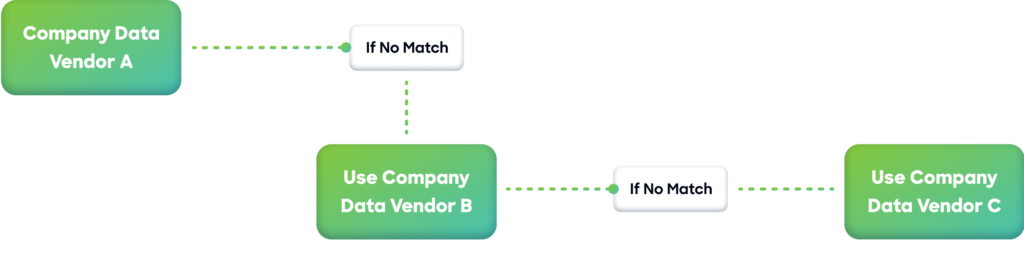
Enrich with Trusted Sources
Multi-vendor enrichment fills gaps in completeness and refreshes stale records. By layering data from multiple providers, you maximize coverage and accuracy.
Tradeshift used ZoomInfo data enrichment and deduplication to enhance their database and improve their sales team's efficiency.
Prevent Errors at the Source
The "1-10-100 rule" explains that it costs 10 times more to correct an error than to prevent one, and 100 times more if an error is not fixed. This illustrates the need to prevent data errors from the beginning.
Proper data orchestration can automatically merge or convert leads, contacts, and accounts based on matching rules that you define.
Security is another consideration here. Adopting secure practices can prevent tampering, meaning your teams can place more confidence in the reliability of your data. This is particularly important when you're gathering data from multiple sources, and relaying the information between different platforms.
Governance basics also matter: assign ownership, define required fields, document definitions, and establish change control processes. These practices create accountability and standards that scale with your team.
Take Control of Your Data Quality
Most data quality management solutions require multiple tools to clean, normalize, transfer, enrich, and match data. Each tool adds complexity. A centralized solution simplifies GTM data maintenance.
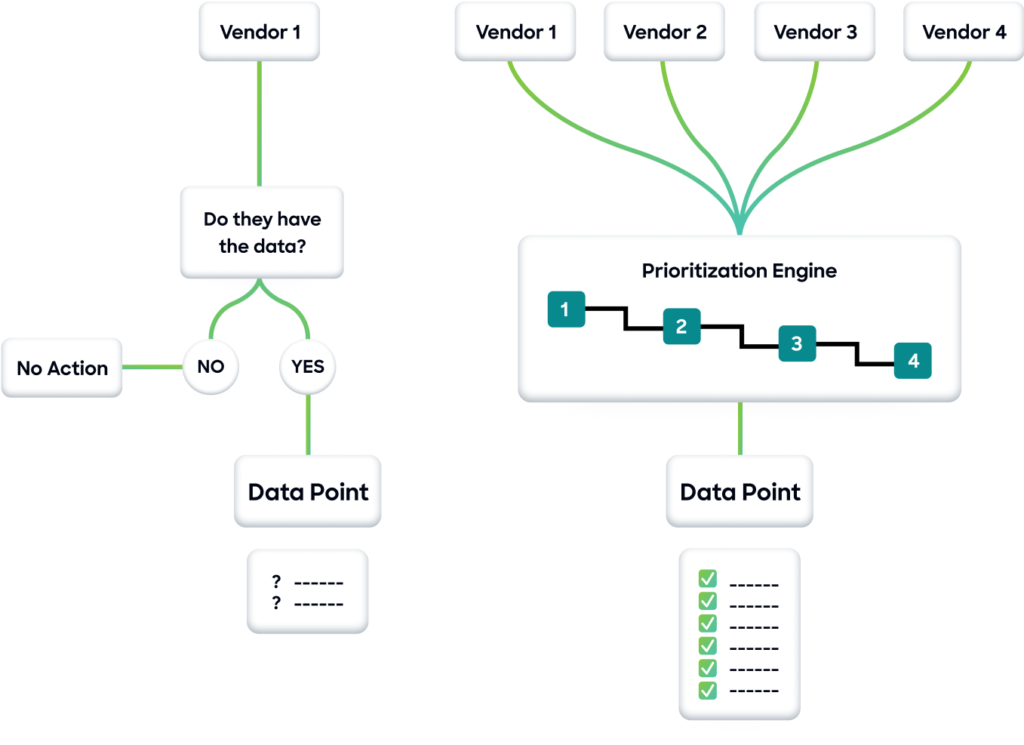
ZoomInfo delivers an integrated approach that eliminates the time-consuming and expensive task of manually cleansing, enriching, and activating multiple datasets. With multi-vendor enrichment, revenue operations teams can build engagement-ready data in one click, rather than spending hours in spreadsheets.
Talk to our team to learn how ZoomInfo can help.


